[Industry Alpha × Aichi Prefecture] Startup Aiming for Labor-saving in Factories and Warehouses Selected for the “New Aichi Innovation Research and Development Subsidy”
Industry Alpha utilizes subsidies to enhance the quality of its proprietary AMR software, contributing to strengthening the competitiveness of Aichi Prefecture’s core manufacturing industry.
Overview
Industry Alpha Inc. (Head Office: Itabashi-ku, Tokyo; Development Base: Nagoya City, Aichi Prefecture; CEO: Takumi Watanabe), which operates a smart factory and warehouse business centered on the development and implementation of low-profile AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) with the mission to “design and realize smart factories and warehouses,” has been selected for Aichi Prefecture’s “New Aichi Innovation Research and Development Subsidy” program for fiscal year 2024.
This subsidy program, operated since 2012 as a measure against industrial hollowing-out, targets large and small to medium enterprises in growth sectors such as next-generation automobiles, aerospace, environment and new energy, health and longevity, information and communication, and robotics. For this fiscal year, 161 companies applied, and 61 were selected.
About the “New Aichi Innovation Research and Development Subsidy”
Aichi Prefecture has operated an innovative subsidy program since fiscal 2012, utilizing the “Industrial Hollowing-Out Countermeasure Tax Reduction Fund” to address the serious issue of industrial hollowing-out.
Industrial hollowing-out refers to the phenomenon where companies, primarily in the manufacturing sector, relocate their production bases overseas, weakening the domestic industrial foundation.
This issue goes beyond mere corporate overseas expansion; it poses a critical challenge shaking the core of Japan’s manufacturing industry due to reductions in domestic employment and the outflow of technological capabilities. Coupled with Japan’s declining population problem, the impact is becoming even more severe.
As a company, Industry Alpha is committed not only to developing and implementing AMRs and their control systems but also to designing fully integrated smart factories and warehouses that enable operations with fewer personnel, thereby contributing to maintaining the competitiveness of Japan’s manufacturing and logistics industries.
Industry Alpha’s Theme under the “New Aichi Innovation Research and Development Subsidy”
About This Initiative
Under this subsidy program, our company will advance software updates for our proprietary AMRs. We aim to improve the quality of the autonomous navigation algorithms that enable the AMRs to estimate their own position and generate routes toward their goals.
What is an AMR?
In the logistics and manufacturing industries, AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) have recently attracted significant attention as a means of automating material transport. Transport methods vary by type of vehicle, including lift-up types that slide under and lift carts for movement, and towing types that hook and pull carts.
Traditional automated guided vehicles (AGVs) commonly used magnetic tapes or QR codes installed on the floor to navigate along fixed paths. However, these systems struggled to adapt flexibly to environmental changes and required reinstallation of magnetic tapes or QR codes whenever layouts were changed.
In contrast, AMRs use LiDAR sensors (infrared-emitting sensors) for navigation, eliminating the need to install guides on floors or elsewhere. This makes AMRs easier to install and modify layouts, enabling flexible movement in collaboration with human workers.
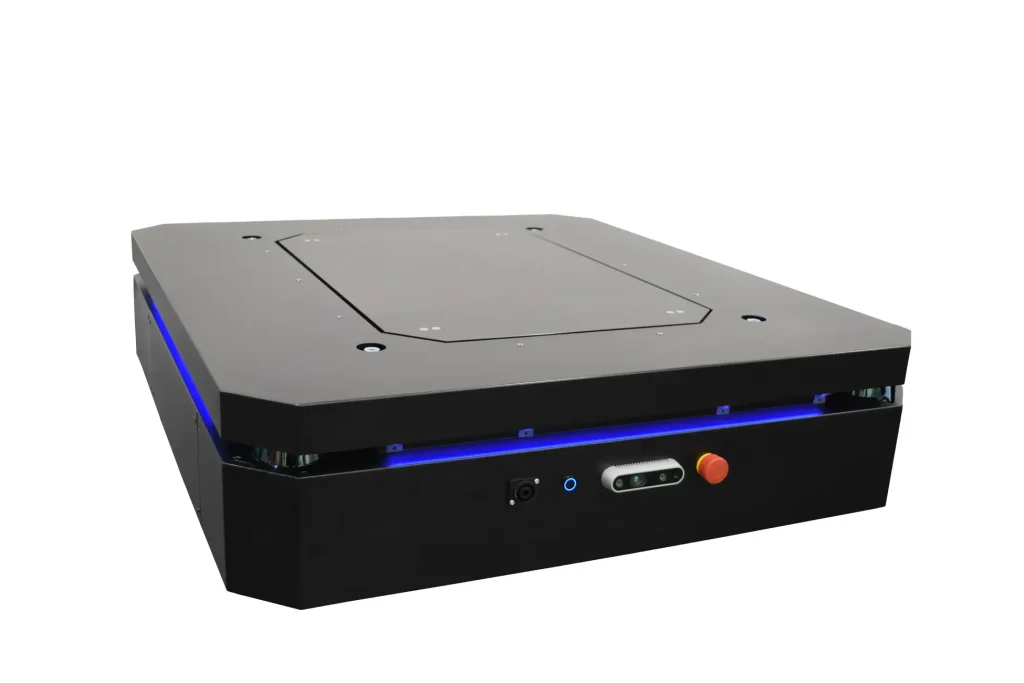

Industry Alpha Low-Profile AMR “Kaghelo”
Challenges and Outlook for AMRs
While traditional AGVs simply follow guides, AMRs must perform complex tasks such as creating environmental maps in advance, continuously estimating their own position, detecting obstacles, and generating routes to their destinations. Therefore, software performance is critically important.
Many of the AMRs currently in use rely on OSS (Open Source Software) for their software. This approach presents several issues:
- Difficulty in Ensuring Quality: It is challenging to guarantee software quality, and appropriate measures to address errors are often unclear.
- Limitations in Detailed Settings: For example, while speed settings may be adjustable, acceleration settings might not be available, limiting the ability to fine-tune parameters for customization.
Industry Alpha is committed to developing proprietary Japanese-made AMRs and has been developing the core software in-house. With the support of this subsidy, we will further strengthen these efforts and contribute to labor-saving in factories and warehouses, which are the foundation of Japan’s manufacturing industry.
